http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/7190107.stm
Seems like a perfect upgrade which would be easy to implement to squeeze more qualtity out of todays binoculars.
T
---------------
'Darkest ever' material created
By Helen Briggs
BBC News science reporter
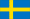
Carbon nanotubes are a basic building block of nanotechnology
The "darkest ever" substance known to science has been made in a US laboratory.
The material was created from carbon nanotubes - sheets of carbon just one atom thick rolled up into cylinders.
Researchers say it is the closest thing yet to the ideal black material, which absorbs light perfectly at all angles and over all wavelengths.
The discovery is expected to have applications in the fields of electronics and solar energy.
Theoretical clues
An ideal black object absorbs all the colours of light and reflects none of them. In theory, it should be possible to make something that approaches the "perfect absorber".
They've made the blackest material known to science
Prof Sir John Pendry
But it has proved difficult to construct an object that does not reflect light at all.
Researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, New York, turned to carbon nanotubes - structures made from carbon, billionths of a metre across, that have unique properties.
Theory suggests that nanotubes might make a super black object, and experts are just starting to test these predictions.
Reporting their findings in the journal Nano Letters, Dr Ajayan, Dr Lin and colleagues say the reflectance of the material is three times lower than previously achieved.
This makes it the "darkest man-made material ever".
"The periodic nanotube structures make an ideal candidate for creating superdark materials, because it allows one to tailor light absorption by controlling the dimensions and periodicities of nanotubes in the structure," said Dr Ajayan.
Commenting on the study, Professor Sir John Pendry, who first predicted that such a discovery might be possible, said the results were promising.
"They've made the blackest material known to science," the theoretical physicist from Imperial College, London, told BBC News.
"The application will be to things like more efficient solar cells, more efficient solar panels and any application where you need to harvest light," he added.