albertonykus
Well-known member
Emslie, S.D. (2020)
Ancient Adélie penguin colony revealed by snowmelt at Cape Irizar, Ross Sea, Antarctica
Geology (advance online publication)
doi: 10.1130/G48230.1
https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/geology/article/doi/10.1130/G48230.1/590932/Ancient-Adelie-penguin-colony-revealed-by-snowmelt
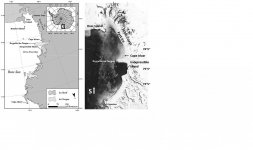
The Ross Sea (Antarctica) is one of the most productive marine ecosystems in the Southern Ocean and supports nearly one million breeding pairs of Adélie penguins (Pygoscelis adeliae) annually. There also is a well-preserved record of abandoned penguin colonies that date from before the Last Glacial Maximum (>45,000 14C yr B.P.) through the Holocene. Cape Irizar is a rocky cape located just south of the Drygalski Ice Tongue on the Scott Coast. In January 2016, several abandoned Adélie penguin sites and abundant surface remains of penguin bones, feathers, and carcasses that appeared to be fresh were being exposed by melting snow and were sampled for radiocarbon analysis. The results indicate the “fresh” remains are actually ancient and that three periods of occupation by Adélie penguins are represented beginning ca. 5000 calibrated calendar (cal.) yr B.P., with the last occupation ending by ca. 800 cal. yr B.P. The presence of fresh-appearing remains on the surface that are actually ancient in age suggests that only recently has snowmelt exposed previously frozen carcasses and other remains for the first time in ~800 yr, allowing them to decay and appear fresh. Recent warming trends and historical satellite imagery (Landsat) showing decreasing snow cover on the cape since 2013 support this hypothesis. Increased δ13C values of penguin bone collagen further indicate a period of enhanced marine productivity during the penguin “optimum”, a warm period at 4000–2000 cal. yr B.P., perhaps related to an expansion of the Terra Nova Bay polynya with calving events of the Drygalski Ice Tongue.
Ancient Adélie penguin colony revealed by snowmelt at Cape Irizar, Ross Sea, Antarctica
Geology (advance online publication)
doi: 10.1130/G48230.1
https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/geology/article/doi/10.1130/G48230.1/590932/Ancient-Adelie-penguin-colony-revealed-by-snowmelt
The Ross Sea (Antarctica) is one of the most productive marine ecosystems in the Southern Ocean and supports nearly one million breeding pairs of Adélie penguins (Pygoscelis adeliae) annually. There also is a well-preserved record of abandoned penguin colonies that date from before the Last Glacial Maximum (>45,000 14C yr B.P.) through the Holocene. Cape Irizar is a rocky cape located just south of the Drygalski Ice Tongue on the Scott Coast. In January 2016, several abandoned Adélie penguin sites and abundant surface remains of penguin bones, feathers, and carcasses that appeared to be fresh were being exposed by melting snow and were sampled for radiocarbon analysis. The results indicate the “fresh” remains are actually ancient and that three periods of occupation by Adélie penguins are represented beginning ca. 5000 calibrated calendar (cal.) yr B.P., with the last occupation ending by ca. 800 cal. yr B.P. The presence of fresh-appearing remains on the surface that are actually ancient in age suggests that only recently has snowmelt exposed previously frozen carcasses and other remains for the first time in ~800 yr, allowing them to decay and appear fresh. Recent warming trends and historical satellite imagery (Landsat) showing decreasing snow cover on the cape since 2013 support this hypothesis. Increased δ13C values of penguin bone collagen further indicate a period of enhanced marine productivity during the penguin “optimum”, a warm period at 4000–2000 cal. yr B.P., perhaps related to an expansion of the Terra Nova Bay polynya with calving events of the Drygalski Ice Tongue.
Last edited: