(Imp sizes. Basic tidy-up. Links. References updated) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[Image:Guadeloupe_Woodpecker.jpg|thumb|550px|right|Photo by {{user|Tord|Tord}}<br>Location: [[Guadeloupe ]]]] | [[Image:Guadeloupe_Woodpecker.jpg|thumb|550px|right|Photo by {{user|Tord|Tord}}<br>Location: [[Guadeloupe ]]]] | ||
==Identification== | ==Identification== | ||
| − | Back and wing coverts are bluish black, while tail and flight feathers on the wing are more brownish black. The breast is reddish to blood-colored (sometimes with an orange tint), while the belly is yellowish-orange. There is no sharp demarkation of plumage colors. Bill is dark, and 20% longer in male than female; this is the only clear sexual dimorphism in this species. Legs are grayish blue, with some yellowish on the feet. Iris is light brown, sometimes with a darker ring distally. Young birds are similar to adults but duller. | + | 24 cm (9½ in) |
| − | + | Back and wing coverts are bluish-black, while tail and flight feathers on the wing are more brownish black. The breast is reddish to blood-colored (sometimes with an orange tint), while the belly is yellowish-orange. There is no sharp demarkation of plumage colors. Bill is dark, and 20% longer in male than female; this is the only clear sexual [[Dictionary D-F#D|dimorphism]] in this species. Legs are grayish blue, with some yellowish on the feet. Iris is light brown, sometimes with a darker ring distally. | |
| + | |||
| + | Young birds are similar to adults but duller. | ||
====Similar Species==== | ====Similar Species==== | ||
| − | The most similar species present in Guadeloupe at the moment probably is the [[Carib Grackle]], which has many structural differences to the woodpecker. | + | The most similar species present in [[Guadeloupe]] at the moment probably is the [[Carib Grackle]], which has many structural differences to the woodpecker. |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| Line 20: | Line 22: | ||
==Taxonomy== | ==Taxonomy== | ||
| − | + | This is a [[Dictionary_M-S#M|monotypic]] species<sup>[[#References|[1]]]</sup>. | |
==Habitat== | ==Habitat== | ||
The Guadeloupe Woodpecker is found in most forest types from sea level to about 1000 meters, however, it is doing better generally in Basse Terre than in Grande Terre. | The Guadeloupe Woodpecker is found in most forest types from sea level to about 1000 meters, however, it is doing better generally in Basse Terre than in Grande Terre. | ||
==Behaviour== | ==Behaviour== | ||
| − | Feeding behavior includes pecking, probing and gleaning. Most of the foraging occurs in the canopy, with males more often utilizing the trunk of a tree, while the female more often utilize branches; when both utilize branches, the male on average chooses heavier branches than the female. Food items sought include both insects and fruit. Most of the insects are taken from dead wood. It will not flycatch contrary to e.g., the [[Jamaican Woodpecker]]. | + | ====Flight Action==== |
| − | + | Notice that contrary to many woodpeckers, this species normally does not undulate in flight. | |
| − | Will normally use a dead tree or branch to make its nest hole. | + | ====Diet==== |
| + | Feeding behavior includes pecking, probing and [[Dictionary G-L#G|gleaning]]. Most of the foraging occurs in the canopy, with males more often utilizing the trunk of a tree, while the female more often utilize branches; when both utilize branches, the male on average chooses heavier branches than the female. Food items sought include both insects and fruit. Most of the insects are taken from dead wood. It will not flycatch contrary to e.g., the [[Jamaican Woodpecker]]. | ||
| + | ====Breeding==== | ||
| + | They breed between January and August. Will normally use a dead tree or branch to make its nest hole at 2-20 m above ground. | ||
==Conservation Concerns== | ==Conservation Concerns== | ||
A current population estimate is around 20000 with an uncertainty of about 4000. That is about the same as in 1994, however, due to habitat destruction and closure of a habitat corridor between the two islands, the outlook for about 20% of the population is rather grim. The species has not been seen traverse water and does not spread any significant distance over non-forested ground. | A current population estimate is around 20000 with an uncertainty of about 4000. That is about the same as in 1994, however, due to habitat destruction and closure of a habitat corridor between the two islands, the outlook for about 20% of the population is rather grim. The species has not been seen traverse water and does not spread any significant distance over non-forested ground. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | # | + | #{{Ref-Clements6thAug15}}#{{Ref-Raffaeleetal03}}# A beautiful monograph: "The Guadeloupe Woodpecker" was written by Pascal Villard, 1999. SEOF ISBN 2-9506548-6-X |
| − | #{{Ref-Raffaeleetal03}}# A beautiful monograph: "The Guadeloupe Woodpecker" was written by Pascal Villard, 1999. SEOF ISBN 2-9506548-6-X | + | #Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive (retrieved January 2016) |
{{Ref}} | {{Ref}} | ||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
| + | {{GSearch|Melanerpes+herminieri}} | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:Birds]][[Category:Melanerpes]][[Category:Maps]] | [[Category:Birds]][[Category:Melanerpes]][[Category:Maps]] | ||
Revision as of 23:40, 30 January 2016
- Melanerpes herminieri
Identification
24 cm (9½ in) Back and wing coverts are bluish-black, while tail and flight feathers on the wing are more brownish black. The breast is reddish to blood-colored (sometimes with an orange tint), while the belly is yellowish-orange. There is no sharp demarkation of plumage colors. Bill is dark, and 20% longer in male than female; this is the only clear sexual dimorphism in this species. Legs are grayish blue, with some yellowish on the feet. Iris is light brown, sometimes with a darker ring distally.
Young birds are similar to adults but duller.
Similar Species
The most similar species present in Guadeloupe at the moment probably is the Carib Grackle, which has many structural differences to the woodpecker.
Distribution
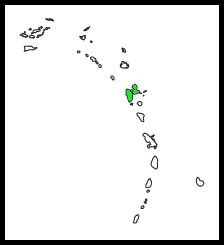
| The Guadeloupe Woodpecker is endemic to Guadeloupe in the Lesser Antilles, where it is found on the two largest islands, the interconnected Grande Terre and Basse Terre. It is the only woodpecker in the Lesser Antilles. | |
| Legend |
Taxonomy
This is a monotypic species[1].
Habitat
The Guadeloupe Woodpecker is found in most forest types from sea level to about 1000 meters, however, it is doing better generally in Basse Terre than in Grande Terre.
Behaviour
Flight Action
Notice that contrary to many woodpeckers, this species normally does not undulate in flight.
Diet
Feeding behavior includes pecking, probing and gleaning. Most of the foraging occurs in the canopy, with males more often utilizing the trunk of a tree, while the female more often utilize branches; when both utilize branches, the male on average chooses heavier branches than the female. Food items sought include both insects and fruit. Most of the insects are taken from dead wood. It will not flycatch contrary to e.g., the Jamaican Woodpecker.
Breeding
They breed between January and August. Will normally use a dead tree or branch to make its nest hole at 2-20 m above ground.
Conservation Concerns
A current population estimate is around 20000 with an uncertainty of about 4000. That is about the same as in 1994, however, due to habitat destruction and closure of a habitat corridor between the two islands, the outlook for about 20% of the population is rather grim. The species has not been seen traverse water and does not spread any significant distance over non-forested ground.
References
- Clements, J. F., T. S. Schulenberg, M. J. Iliff, D. Roberson, T. A. Fredericks, B. L. Sullivan, and C. L. Wood. 2015. The eBird/Clements checklist of birds of the world: v2015, with updates to August 2015. Downloaded from http://www.birds.cornell.edu/clementschecklist/download/
- Raffaele, H, J Wiley, OH Garrido, A Keith, JI Raffaele. 2003. Birds of the West Indies. Princeton: Princeton Univ. Press. ISBN 978-0691113197
- A beautiful monograph: "The Guadeloupe Woodpecker" was written by Pascal Villard, 1999. SEOF ISBN 2-9506548-6-X
- Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive (retrieved January 2016)
Recommended Citation
- BirdForum Opus contributors. (2024) Guadeloupe Woodpecker. In: BirdForum, the forum for wild birds and birding. Retrieved 26 April 2024 from https://www.birdforum.net/opus/Guadeloupe_Woodpecker